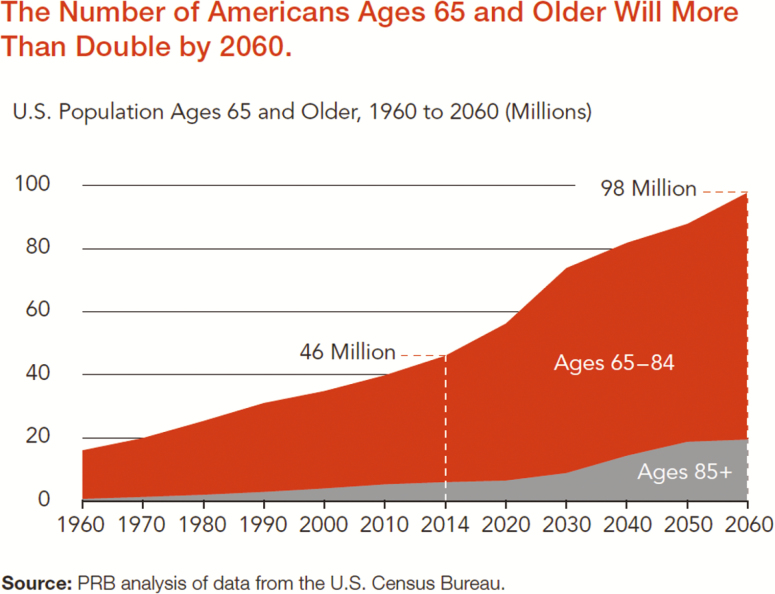
Background and ObjectivesThe public well being system in America-at all levels-has comparatively few specialised initiatives that prioritize the well being and well-being of older adults. And when public well being does tackle the wants of older adults, it’s typically as an afterthought.
In session with leaders in public well being, well being care, and growing old, an progressive Framework for an Age-Friendly Public Health System (Framework) was developed outlining roles that public well being might fulfill, in collaboration with growing old companies, to handle the challenges and alternatives of an growing old society.
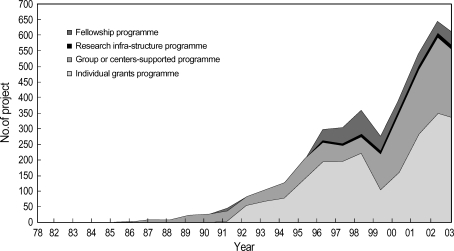
Research Design and MethodsWith management from Trust for America’s Health and The John A. Hartford Foundation, the Florida Departments of Health and Elder Affairs are piloting the implementation of this Framework inside Florida’s county well being departments and on the state degree.
The county well being departments are increasing information assortment efforts to determine older grownup wants, creating new alliances with growing old sector companions, coordinating with different companies and group organizations to implement evidence-based packages and insurance policies that tackle precedence wants, and aligning efforts with the age-friendly communities and age-friendly well being techniques actions.
Results and Discussion and ImplicationsThe county well being departments in Florida collaborating within the pilot are leveraging the Framework to increase public well being observe, packages, and insurance policies that tackle well being companies and well being behaviors, social, and financial components and environmental circumstances that permit older adults to age in place and reside more healthy and extra productive lives.
The mannequin being piloted in Florida may be tailor-made to satisfy the distinctive wants of every group and their older grownup inhabitants.
Antimicrobial and antibiofilm exercise of the EeCentrocin 1 derived peptide EC1-17KV through membrane disruption.
The antibiotic resistance and biofilm formation of pathogenic microbes exacerbate the difficulties of anti-infection remedy within the clinic. The structural modification of antimicrobial peptides (AMP) is an efficient technique to develop novel anti-infective brokers.Seventeen amino acids (AA) within the longer chain of EeCentrocin 1 (from the edible sea-urchin Echinus esculentus) had been truncated and underwent additional modification.
To produce lead peptides with low toxicity and excessive efficacy, the antimicrobial exercise or cytotoxicity of peptides was evaluated in opposition to varied multidrug-resistant micro organism/fungi or mammalian cells in vivo/ in vitro. In addition, the soundness and modes of motion of the lead peptide had been investigated.EC1-17KV displayed potent exercise and an expanded antimicrobial spectrum, particularly in opposition to drug-resistant gram-negative micro organism and fungi, attributable to its enhanced amphiphilicity and web cost.
In addition, it reveals bactericidal/fungicidal exercise and successfully elevated the animal survival charge and mitigated the histopathological harm induced by multidrug-resistant P. aeruginosa or C. albicans in contaminated mice or G. mellonella. Moreover, EC1-17KV had a poor capacity to induce resistance in micro organism and fungi and exhibited fascinating high-salt/high-temperature tolerance properties. In micro organism, EC1-17KV promoted divalent cation launch to wreck bacterial membrane integrity.
In fungi, it modified C. albicans membrane fluidity to extend membrane permeabilization or decreased hyphal formation to suppress biofilm formation.EC1-17KV is a promising lead peptide for the event of antimicrobial brokers in opposition to antibiotic resistant micro organism and fungi.This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81673483, 81803591); National Science and Technology Major Project Foundation of China (2019ZX09721001-004-005);
National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFA0902000); “Double First-Class” University mission (CPU2018GF/GY16); Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province of China (No. BK20180563); and A Project Funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.